Running tests¶ The test database ¶. Tests that require a database (namely, model tests) will not use your “real” (production) database. Order in which tests are executed ¶. All TestCase subclasses are run first. Then, all other Django-based tests (test. Rollback emulation ¶. Any initial data. In this tutorial, you created a test suite in your Django project, added test cases to test model and view logic, learned how to run tests, and analyzed the test output. As a next step, you can create new test scripts for Python code not in models.py and views.py. Django’s test client has a different focus. In short: Use Django’s test client to establish that the correct template is being rendered and that the template is passed the correct context data. Use in-browser frameworks like Selenium to test rendered HTML and the behavior of.
November 11, 2017While PyCharm Pro might be the most popular IDE for Python development, the community version supports neither Django nor JavaScript . VSCode is a free opensource alternative which has pretty good Python support.
Python is supported in VSCode using an extension. A quick start guide on the extension can be found here. It has builtin support for unittest, pytest, and Nose.
You can find information about debugging Django using VSCode here. The extension does not have builtin support for Django UnitTests, but we can use pytest to run Django UnitTests. Please make sure that you have installed pytest and pytest-django. They can be installed using pip.
Shell12[pytest]DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=myproject.settingsWell, That’s all the settings required to run django unit tests. Click the ‘Run Tests’ button on the status bar and select ‘Run All Unit Tests’ from the context menu.
Tests will run and the result summary will be displayed on the output tab. If the test output is not visible, select ‘Run Tests’ and select ‘View Unit Test Output’. Summary of the tests can be viewed from the status bar as well.
Plug and play continuous integration with django and jenkins
There are a lot of ways to enable continuous integration with your django project. But most of them require a lot of time to configure and setup ci server and make changes in your django project.
This tutorial introduces a new way to enable continuous integration for django project, with minimal projects modifications by means of with django-jenkins.
Previously, ad-hoc integration django with jenkins required using nose testing frameworks instead of django native unittests. Since nose project uses custom test loader it leads to a lot of problems with django code - duplicate signals subscriptions, module loading and other test-only realted errors. Django-jenkins uses a standard unittest runner, so the code under test works like in production. No difference between django-jenkins run and manage.py test so keeps your hands free for real work.
Configuring django project¶
To enable django_jenkins you need only to add django_jenkins to INSTALLED_APPS in settings.py.
Running
will do the same job as
but also will create reports folder in the root of your django project with jenkins parsable pylint, test coverage and tests reports.
Django-jenkins have support for several other testing tools/ To enable it, you should include tools task to JENKINS_TASKS settings variable.
Please, note that corresponding task tool should be installed on jenkins server manually. Please refer to django-jenkins README for specific task dependencies list.
In order to get the right coverage, 'django_jenkins' app should be included as early as possible in INSTALLED_APPS
This tutorial doesn’t cover the library dependency management and deploying your django project on external server. Basically you could setup the CI server as you did in your local environment.
But if you prefer automatically installation and configuration dependencies on CI server, you could easily add virtalenv support for your project.
Add requirements to your requirements.txt file:
Running
will create local folder env with the required libraries for your project. Running those commands on other servers will help to sync the external dependencies.
Configuring jenkins¶
After a fresh Jenkins installation, you’ll need to install two required plugins:

- Violations plugin for parsing
pylintreports and - Cobertura Plugin for showing the code coverage.
Install these plugins via ManageJenkins->ManagePlugins->Available.
Start new job with creating free-style project:
After configuring the repository access, set up the build trigers. Poll SCM will run the build if any changes in repository are found. The line */5**** means checking repository every 5 minutes.
Select Addbuildstep->Executeshell. Add comands to setup environment and the run tests command
Specify the location of test reports - reports/TEST-*.xml and reports/lettuce.xml (in case you are using lettuce tests) files.
CHANGED in 0.13.0:: test reports from TEST-*.xml now stored in one file: junit.xml.
Configure locations of violations reports:
Test coverage reports are in reports/coverage.xml
That’s all!
Results¶

Press BuildNow and see what you’ve got:
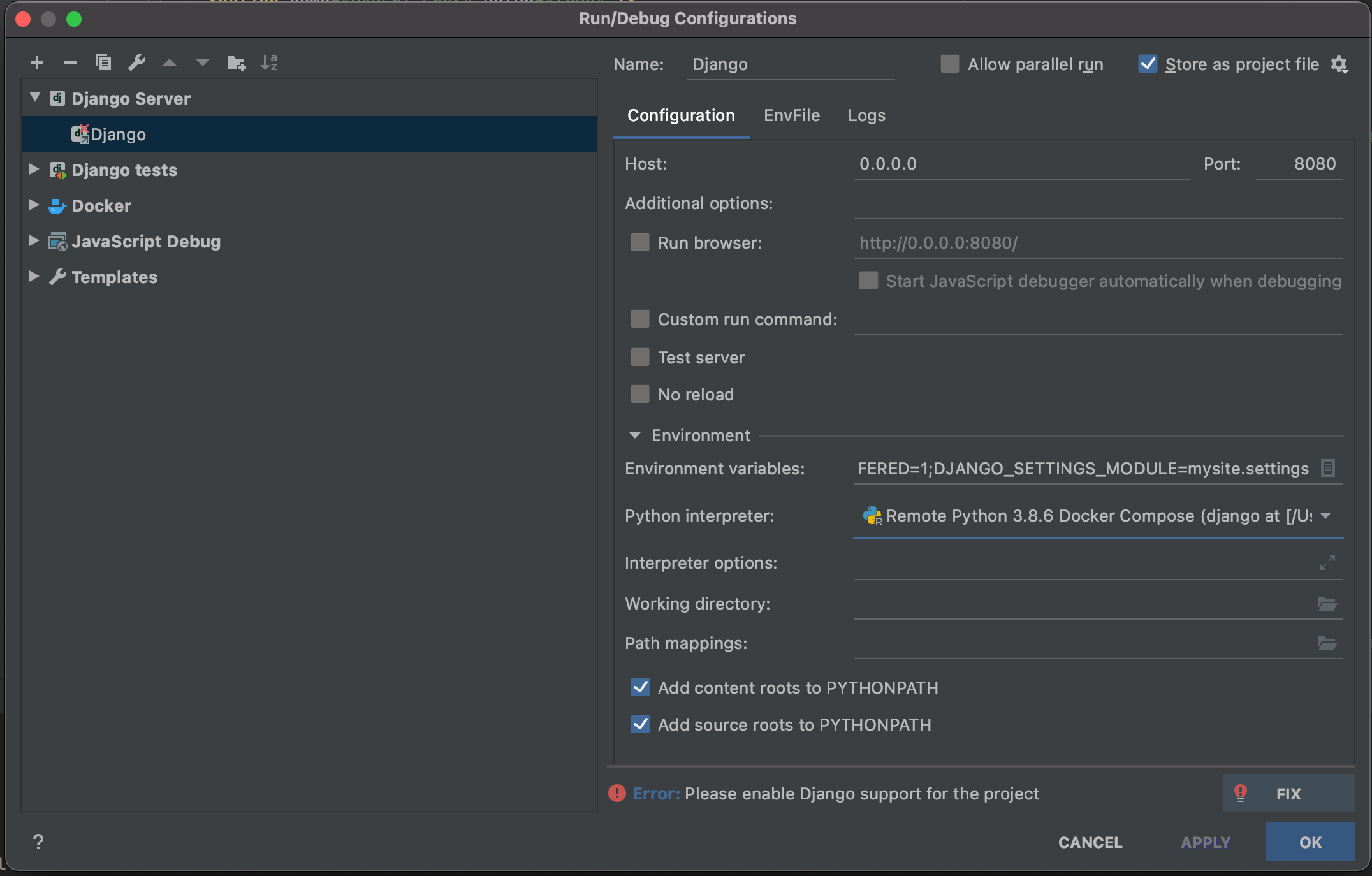
Run Django Tests In Pycharm
Pylint and other lint tools reports for each builds, shows what warning/errors are new for each build.
Nice code coverage reports, showing the total coverage, and colored file listing.
Run Django Tests Positive
And of course the test results and output.